Antidepressant Side Effects: What You Need to Know Before Starting Treatment
When you start taking an antidepressant, a medication used to treat depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders by balancing brain chemicals. Also known as antidepressive agents, these drugs can help you feel like yourself again—but they don’t work the same for everyone. Many people expect immediate relief, but the truth is, side effects often show up before the benefits do. That’s normal. But not all side effects are harmless. Some are warning signs you can’t ignore.
Most SSRIs, a common class of antidepressants that increase serotonin levels in the brain. Also known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors like sertraline or escitalopram cause nausea, headaches, or trouble sleeping in the first few weeks. SNRIs, another major class that affect both serotonin and norepinephrine. Also known as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like venlafaxine can raise blood pressure or cause dry mouth. These aren’t rare. In fact, up to half of people taking them experience at least one side effect early on. What’s more, stopping abruptly can trigger withdrawal symptoms, a set of physical and mental reactions that happen when you suddenly stop taking an antidepressant. Also known as discontinuation syndrome—dizziness, electric shock feelings, or even flu-like symptoms. That’s why you never quit cold turkey.
Some side effects are easy to miss. Weight gain. Low sex drive. Feeling emotionally flat. These aren’t listed as "serious," but they can make life harder than before you started. And then there are the dangerous ones: confusion, rapid heartbeat, or severe agitation—signs of serotonin syndrome, a rare but life-threatening reaction that can happen if you mix antidepressants with other drugs like certain painkillers or herbal supplements. It’s not just about the pill you’re taking. It’s about everything else in your system.
What you’ll find below are real stories and clear facts from people who’ve been through this. We cover how to tell if a side effect is temporary or a red flag. How to talk to your doctor without sounding like you’re overreacting. What alternatives exist if the first drug doesn’t work. And how to avoid common mistakes that make side effects worse. This isn’t theoretical. These are the issues people face when they start treatment—and what actually helps.
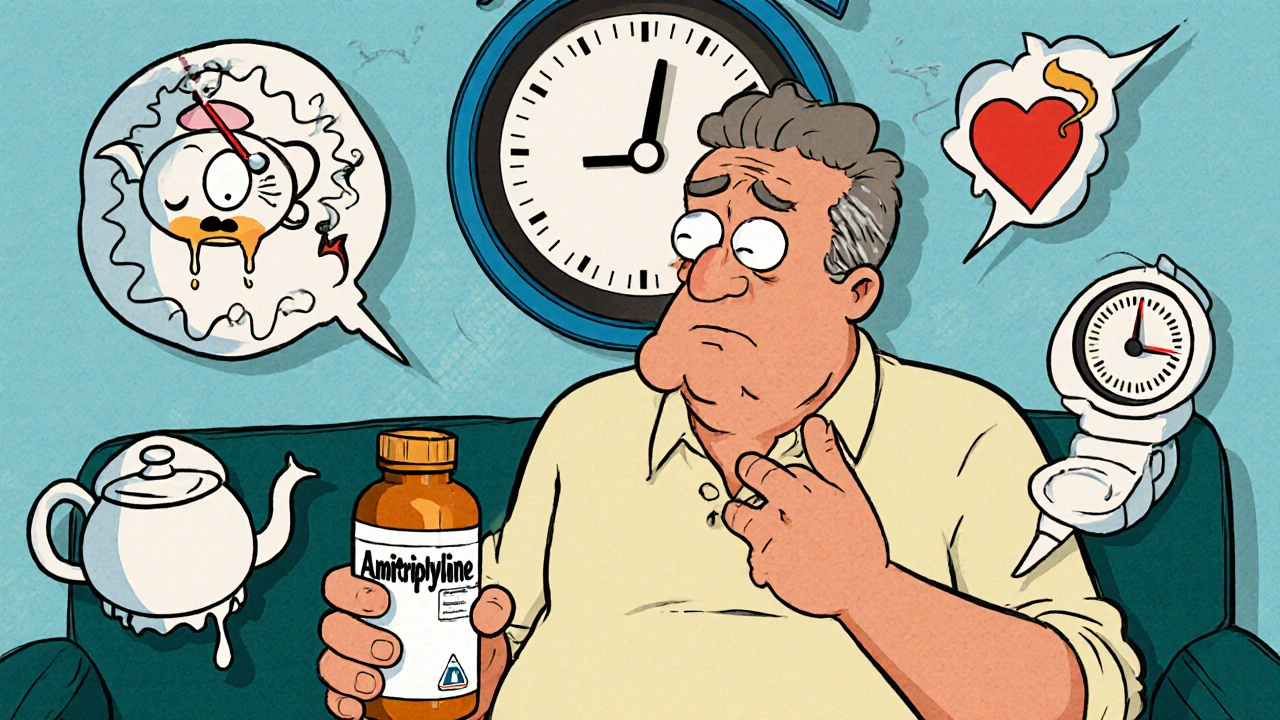

Tricyclic Antidepressant Side Effects: Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline, and More
Amitriptyline and nortriptyline are still used for depression and nerve pain, but their side effects-dry mouth, dizziness, heart risks, and cognitive issues-make them dangerous for many. Learn when they’re worth the trade-off.